Failures Happen, Learn from Them
If you’ve made it here, something probably went wrong.
And you don’t want it to happen again.
Failure is sometimes inevitable. All we can do is learn from it and fix the issues so it doesn’t happen again. But how do you know what to fix?
When something fails, you need to know exactly why it failed. The only thing worse than not fixing the issue is fixing something that was never a problem in the first place!
The first thing that we do when we’re analyzing the failure is determine the right tool to use. We have an arsenal of tools, including:
- FMEA
- Fault Tree
- Kepner Tregoe
- Why Staircase
No one tool is universal. The failure analysis tool needs to be chosen based on the scenario. Sometimes, using more than one tool is appropriate.
If the failure is extremely critical (e.g. failure of a high risk significant component at a nuclear plant), then make sure an independent failure analysis is performed. Using an independent failure analysis is like a double-blind study. Nobody knows the answer at first, and the results are only reliable if both parties come to the same conclusion independently.
Independent failure assessments lead to highly defendable results. In our experience, if independent assessments are done, regulatory bodies (like the NRC) are much more accepting of the results.
Substantiate Your Claims
Just the facts
The failure analysis is only as good as the facts used to back it up, and experts should be careful to separate fact from opinion.
Recreate the Event
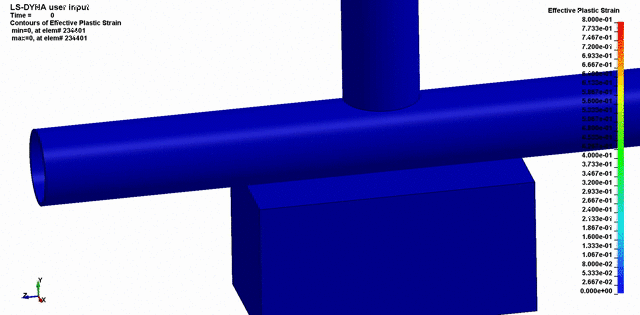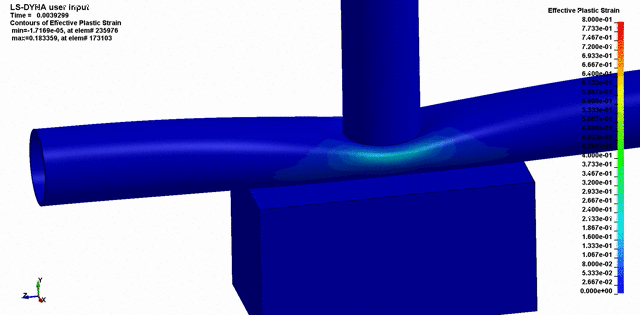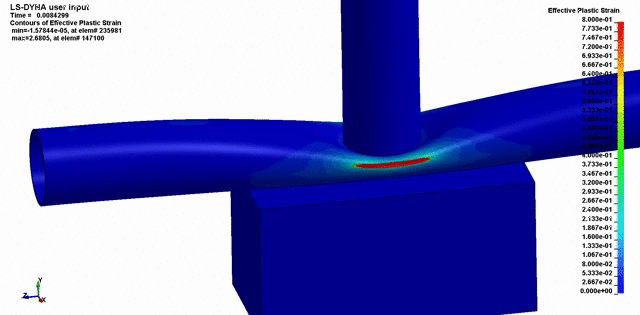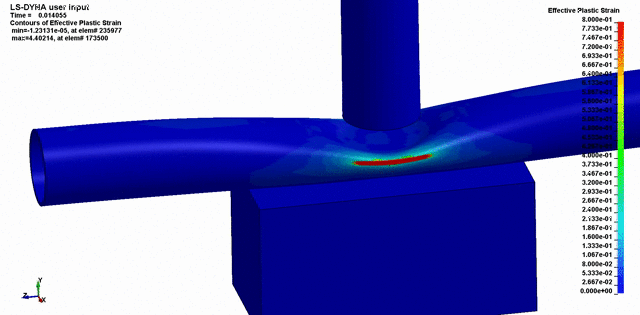
Once the conditions of the event are known, testing and simulation can often be used as a powerful tool in showing how the event took place, and validating how the failure occurred.
We’ve used Finite Element Analysis, Computation Fluid Dynamics, scaled models, and other engineering techniques to simulate the conditions leading up to failure of components. This is incredibly powerful because it can often be used to prove or disprove all the conditions surrounding the failure.
Expert Witness
If a failure has caused your organization to need an expert witness, give us a call. We’re licensed in New York state, and we’d be happy to provide our expert opinion, backed by formal analysis.
Experience
We’ve outlined some of our recent failure analysis experience below.
[wp_blog_designer id=”8″]



